Listen to this blog
Digital Product Passports & the Circular Value Chain
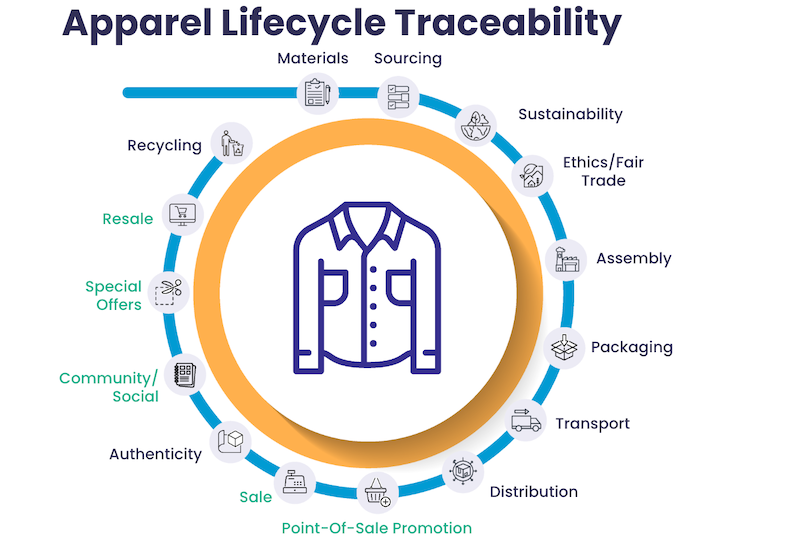
A Digital Product Passport is a cutting-edge tool that enables businesses to collect, store, and share detailed information about a product’s lifecycle. From raw material sourcing to manufacturing processes, and from usage to disposal and recycling, digital product passports provide a comprehensive digital record of a product's journey. This passport is designed to enhance transparency, improve decision-making, and support sustainable practices across various stakeholders, including manufacturers, resellers, consumers, authorities, and NGOs. This information can be accessed via GS1 Digital Links found on products; including BL.INK’s GS1 Digital Link offering which can include a dynamic microsite, otherwise known as a digital product passport.
What is a Digital Product Passport?
A Digital Product Passport is essentially a "digital twin" of a physical product that securely records and shares data related to the product’s lifecycle. Think of a digital product passport as a representation of the product, sharing key information, ingredients, and production details about the physical products. Users can easily access valuable information by scanning the QR code on a product or its packaging. This information includes details on durability, reparability, recycled content, and availability of spare parts, among other attributes. It can be shared on the product itself or the product's packaging.
Digital product passports are intended to solve the information problem regarding circularity and impact on natural resources by acting as a gateway to limitless links to pages or sites that go in-depth about these topics. When a consumer visits a digital product passport, they can discover the company's stance on sustainability, country of origin, fair trade practices. Furthermore, digital product passports help manufacturers make their sustainability practices available to public authorities and inspectors, contributing to the overall goal of fostering a sustainable business ecosystem and helping products prove and sustain compliance.
Consumers can also access digital product passports to get real-time practical information, such as nutritional and allergy information, installation or dosing details, and even how to recycle or dispose of the product after use—helping consumers make informed decisions. Why do we need Digital Product Passports?
Driving the Circular Economy
The transition to a circular economy, where products and materials are continuously reused, repaired, and recycled, is essential for sustainable growth. The European Green Deal (EGD) highlights the economic and environmental benefits of this transition, aiming to create resilient economies through sustainable resource utilization. The implementation of digital product passports is a crucial step towards achieving these goals by providing detailed information about a product’s lifecycle and environmental impact.
Overcoming Challenges in Resource Management
Currently, global and European economic resource flows follow a linear trajectory, leading to significant resource waste. Nearly 90% of material resources used within the EU are discarded after their initial use. Digital product passports address this issue by enabling a more holistic approach to product design, production, distribution, usage, and collection. This approach minimizes resource extraction, waste generation, and carbon emissions, supporting the development of a sustainable and circular economy.
Ensuring Compliance and Enhancing Transparency
Digital product passports play a pivotal role in ensuring compliance with sustainability regulations, such as the Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR). By providing a unified framework for capturing and sharing product data, digital product passports enhance transparency and accountability across the supply chain. This transparency not only benefits regulators and policymakers but also empowers consumers to make more informed purchasing decisions.
Benefits of Digital Product Passports
For Businesses
- Enhanced Data Credibility: Digital product passports link directly to certification providers, ensuring that the accompanying certificates are highly credible and trustworthy. This mitigates concerns regarding outdated or unverified eco-labels and sustainability certificates.
- Increased Business Opportunities: The shift towards a circular economy opens up new business models, such as product-as-a-service, repair services, and resale markets. Digital product passports provide the necessary data to support these models and unlock additional revenue streams.
- Improved Supply Chain Transparency: Digital product passports provide detailed insights into the materials, methods, and processes used in product manufacturing, ensuring responsible sourcing and production. This transparency benefits all stakeholders in the value chain, from suppliers to consumers.
- Validated Green Claims: Digital product passports help businesses validate their sustainability claims, reducing the risk of greenwashing and building consumer trust. By recording events throughout a product's lifecycle, businesses can prove the authenticity and sustainability of their products.
- Operational Efficiency: By streamlining data collection and sharing, Digital product passports improve operational efficiency and reduce costs. They also minimize disruptions in data flow along the supply chain, contributing to overall business growth and stability.
For Consumers
- Informed Purchasing Decisions: Digital product passports empower consumers to make informed choices by providing transparent information about a product’s sustainability, environmental impact, and recyclability. This transparency enhances buyer confidence and loyalty.
- Maximized Product Value: With access to detailed product information, consumers can verify the authenticity and quality of their purchases. This is particularly beneficial in the resale market, where the legitimacy of second-hand goods can be easily confirmed.
- Protection Against Greenwashing: Digital product passports help consumers identify false sustainability claims, ensuring that they support truly eco-friendly brands. This protection fosters a more honest and accountable market.
- Recognition of Carbon Footprint: Consumers can use digital product passports to track the carbon footprint of their purchases, allowing them to make more environmentally responsible choices. This information can also incentivize sustainable behavior, such as recycling and repairing products.
For Policy Makers and Governing Bodies
- Verification of Compliance: Digital product passports provide a unified basis for tracking business compliance with sustainability initiatives. This enables policymakers to benchmark key performance indicators (KPIs) and take necessary actions to enforce regulations.
- Driving Sustainability: By enforcing transparency and accountability, Digital product passports help drive sustainability across industries. They reduce the prevalence of greenwashing and ensure that businesses adhere to environmental standards.
- Facilitating Circular Economy Goals: Digital product passports support the goals of the Circular Economy Action Plan (CEAP) by promoting sustainable production and consumption practices. They provide the data needed to evaluate and enhance circularity within various sectors.
Key Considerations for Implementing Digital Product Passports
Data Collection and Management
Effective data management is crucial for the success of digital product passports. The data collected should cover various aspects of the product lifecycle, including:
- General Information: Product ID, batch numbers, reference numbers, weight/volume, manufacturing location and dates, and manufacturer operator ID.
- Source Data: Information on raw materials and components, chemicals, plastics, ingredients, and substances used in manufacturing.
- Environmental Footprint: Data on carbon footprint, waste generation, energy consumption, and emissions.
- Ownership and Maintenance: Details on past and current ownership, repair histories, and event audit trails.
- Documentation and Instructions: Digital versions of warranties, service records, insurance documents, and end-of-life disposal instructions.
Data Sharing and Accessibility
Given the broad range of stakeholders involved in a product's lifecycle, a flexible approach to data sharing and accessibility is essential. Under the ESPR, key stakeholders who should have access to digital product passports include:
- Customers
- Manufacturers
- Importers
- Distributors
- Repairers
- Remanufacturers
- Recyclers
- Market surveillance authorities
- Customs authorities
- Civil society organizations
- Trade unions
- The European Commission
Permissions to access, modify, or update data will be defined by the European Commission, ensuring data security and privacy.
Technological Infrastructure
The success of digital product passports relies on robust technological infrastructure that can collect, manage, and share sustainability data from various sources. This infrastructure must be capable of:
- Ensuring Data Accuracy: Accurate data collection and management are crucial for the credibility of digital product passports.
- Supporting Long-Term Accessibility: Digital product passports need to be accessible throughout a product’s lifecycle, which could span several years or even decades. This requires a robust infrastructure that can withstand technological changes and multiple ownerships.
Regulatory Compliance
Businesses must ensure that their digital product passports comply with relevant regulations, such as the ESPR. This involves:
- Staying Informed: Keeping up-to-date with the latest regulatory requirements and guidelines.
- Implementing Necessary Changes: Adapting business practices and data management systems to meet compliance standards.
- Collaborating with Stakeholders: Working with suppliers, partners, and regulators to ensure a seamless transition to digital product passport implementation.
Digital product passports promote sustainability and help brands connect with consumers transparently
Digital product passports represent a significant advancement in promoting sustainability and transparency across industries. By providing detailed information about a product’s lifecycle, digital product passports empower consumers to make informed choices, support businesses in achieving their sustainability goals, and facilitate regulatory compliance. As the adoption of digital product passports continues to grow, they will play a crucial role in driving the transition to a circular economy and fostering a sustainable future for all.
At BL.INK, we use technology to simplify complex data and communication challenges. Our GS1 Digital Link solution and BL.INK CXP—a no-code CMS that creates dynamic microsites from data silos—streamline the digital product passport data process and make it easy for consumers to access product information directly from QR codes on your products. We'd love to show you how our solutions make your life easier. Let's talk.